21CFR Part 11 compliance
The 21CFR Part 11 compliance is supported, starting with visionCATS 2.0. It includes many administration and security features described in this section.
Note
This section does not describe the 21CFR Part 11 itself nor its implementation. It provides only a user-oriented view of its impacts in visionCATS.
Understanding the logging features
visionCATS contains many logging features, but the logging features related to the 21CFR Part 11 compliance consist of 2 separate loggers:
The System Logger, available at the application-wide level.
The HPTLC Logger, available in Method, Analysis and Comparison files.
All the important actions made in the visionCATS software are logged in the System Logger, whereas modifications made directly to an HPTLC item are logged in its own HPTLC Logger. However, there are overlapping actions, like some actions made in the Explorer view. For example, creating a new method inserts a log entry in the System Logger because there is a modification to the Explorer view, and a log entry in the HPTLC Logger of the newly created method to detail all its characteristics.
System logger
The System Logger logs automatically the important actions made by the users of the visionCATS software. It therefore builds a global history of the activity of its users. Each important action results in a new line in the System Logger, which contains essentially the timestamp of the action, the user and the message. The messages are also categorized in a 2-levels hierarchy to facilitate future searches.
System Logger data are displayed in two places:
The System Log toolbox (go to ). It displays the messages of the last 24 hours. This toolbox is accessible to all users and does not require the 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance option. It is designed like a live viewer, updated automatically, useful to follow the activity of the current visionCATS installation.
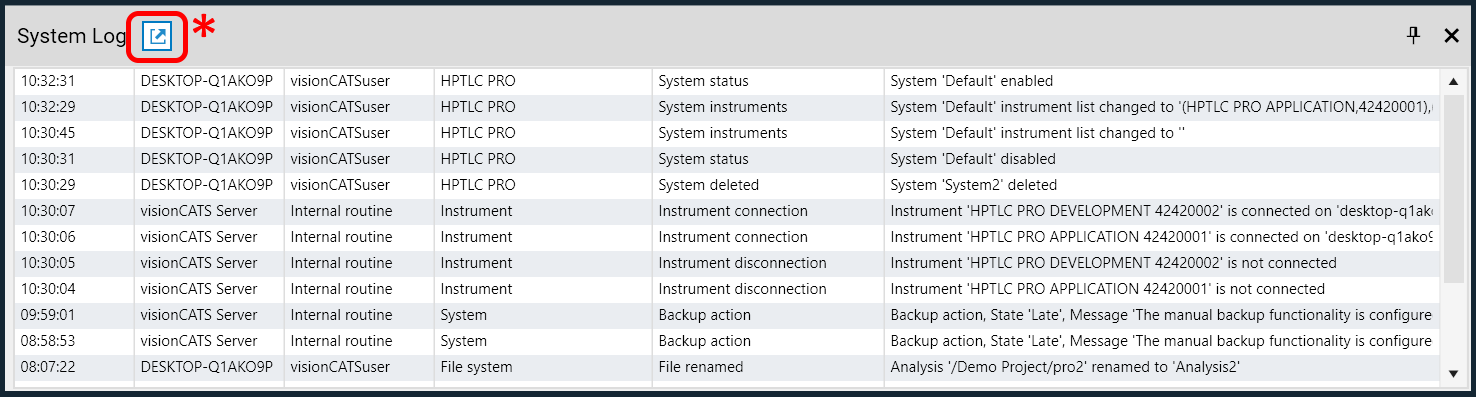
The full view is available by clicking the button (*) in the header (see below).
The full System Logger view (go to ). Available only with the 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance option, this view has the following features:
Filtering by
client (combo box): the machine name when the action occurred in the visionCATS application, or ‘visionCATS Server’
user (combo box): the user login when User Management is activated (‘visionCATSuser’ is the default user otherwise)
category and action (checkboxes and combo boxes)
date (date filter section) : the table shows by default the entries of the last week, but, by expanding the date range, all the entries since the installation of the system are accessible
text (text box) : textual search through the messages
Sorting, by clicking on the column headers (the table is by default sorted by date)
Pagination, by using the paginator on top of the table
 Refresh the display by reloading logs
Refresh the display by reloading logs Export (CSV export of the items, taking account of the current filter)
Export (CSV export of the items, taking account of the current filter)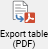 Export (as PDF report, taking account of the current filter)
Export (as PDF report, taking account of the current filter)
Client and User may not always refer to human users. The visionCATS software itself can record messages in the system logger when an important operation occurs without any user interaction. For example:
Messages written by the backup scheduler (see Scheduling backup),
Instrument connection/disconnection,
When a visionCATS application crashes, the visionCATS server closes the connection with the client after some time and logs the operation in the system logger.
HPTLC Logger
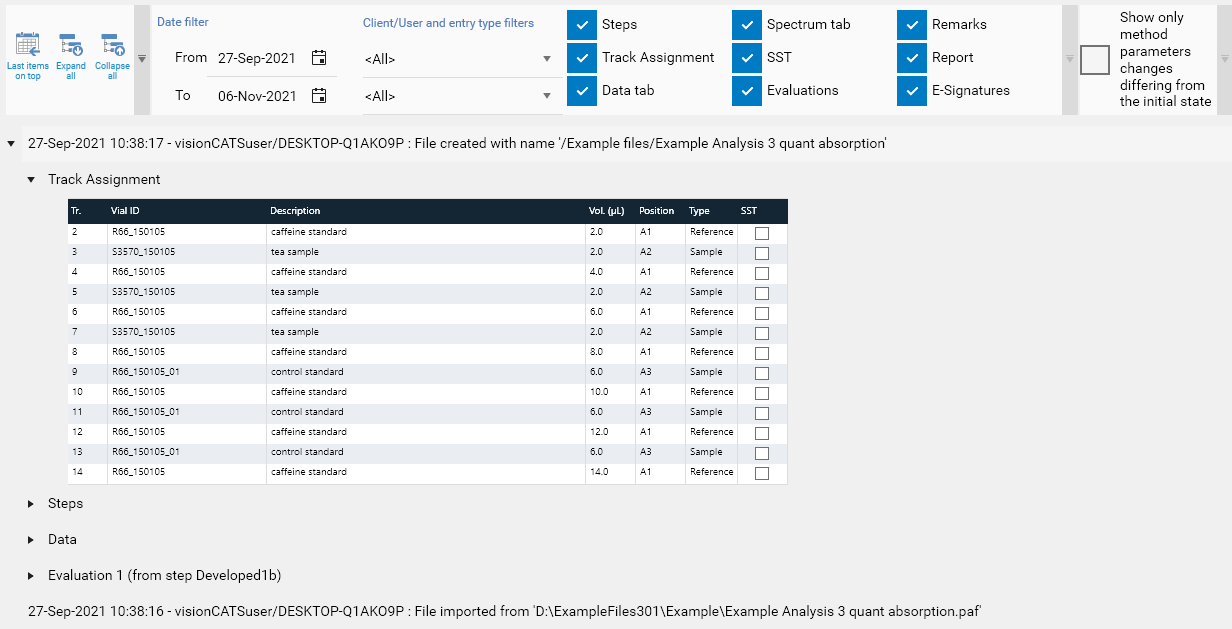
The HPTLC Logger (for methods, analysis and comparisons) logs all the modifications made to each HPTLC item in a tree. Each log item corresponds to an action (for example: the creation of the item, the execution of a step or the ‘save’ action after having modified some parameters) associated with a timestamp and the user who has issued the modification. When the value of a parameter is modified, the tree shows the old and the new value. More complex modifications, like lists or table modifications, are handled case by case but, at least, the log entry will always indicate that there was a change and display the new values. Globally, the structure of the tree follows the tab structure of the HPTLC item. For example, in case of an analysis, modifications are grouped by their location (Steps/Chromatography, Data, Spectrum, SST, Evaluation) and inside each evaluation, modifications are further grouped by tab (Definition, Integration, etc.).
Note
The Show only method parameters changes differing from the initial state option, introduced in visionCATS 3.2, is available only in analysis files. It allows to filter the log entries to display only the ones having changes in method parameters compared to the state of the analysis when it was created. Method parameters include all the information normally defined in method files:
Steps and their parameters
Track Assignment table fields available in the method (Description, Volume, Type and SST fields)
Definition of SST parameters
Definition of evaluation parameters (substances definition, integration parameters, display and limit test options definitions, substances groups definitions)
In case of comparison files, the functionality is similar. The structure of a report entry follow the image/profile/spectrum/report structure.
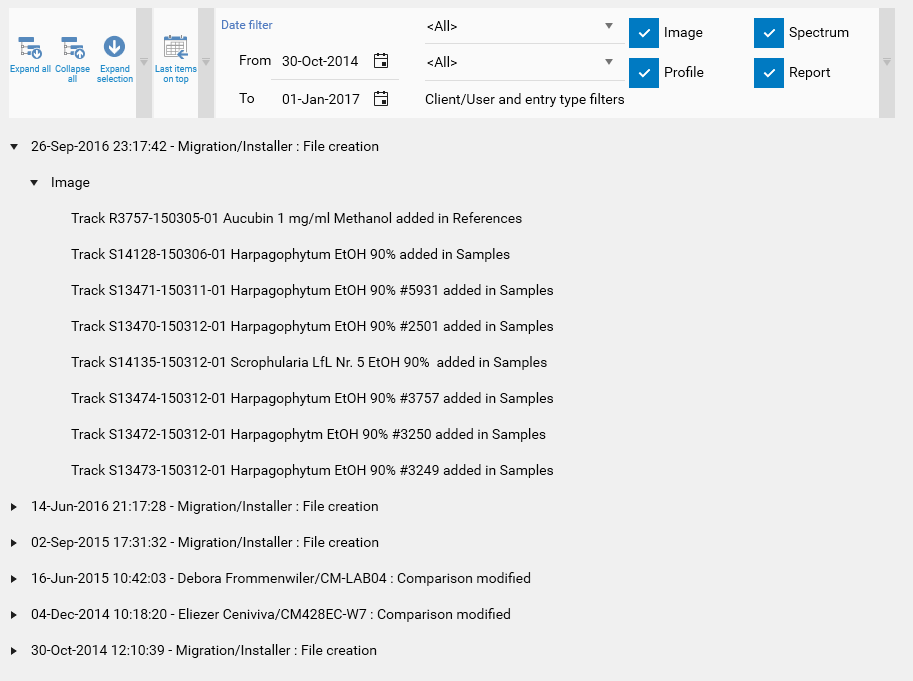
To access the HPTLC Logger of an HPTLC item, open the HPTLC item (typically via the Explorer view) and then open the Log tab. This tab shows the history of all modifications made to the item. The following features are provided:
Navigate in the tree by expanding/collapsing elements and/or by using the helper buttons
Invert the chronological ordering of the log entries
Filter by date, user, area of modification
Note
From visionCATS 3.2, aborted steps data, like images and profiles, are visible in the HPTLC Logger
Deletion of data
Note
This feature is only available on visionCATS installations where the 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance option is active.
By default, deleting an HPTLC item or a folder causes all its data to be lost. visionCATS administrators can modify this behavior by going to and checking/unchecking the corresponding options in the Deletion of data section:

Note
Starting with visionCATS 3.2, the Archiving option replaces the options referred as obsolete in previous versions. During the migration from 3.1 to 3.2, obsolete files are automatically marked as archived.
The possible selection options are described in the following table:
Desired effect |
Solution |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Files and folders archiving
Apart from blocking the access to the Delete function on Explorer files and folders, the Archiving option provides the following benefits:
On large installations, the Explorer can become large and loading visionCATS can be slow. Archiving old or not used files/folders allows visionCATS to load faster, as archived items are not loaded if they are not displayed.
By archiving old or not used items, users can focus on actively used files.
Using the archiving feature requires some configuration and implies specific rules. Both are explained in this section.
In order to use the Archiving feature, the Archiving box must be checked and the current user must have the Archive/restore right (see Users and groups rights). The Archive option is then available on files and folders in the Explorer view (see Menu File):
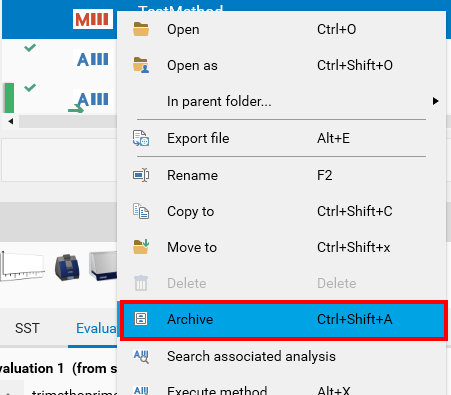
By default, archived items are not displayed in the Explorer. In other words, performing the Archive will make the item disappear. In order to browse archived items, users can check the Show “Archived” items in explorer user option (see User Options). The archived files/folders then appear, after visionCATS is restarted:

Archived files are always in read-only mode by convention. As a result, they can be opened, moved or copied, but most functions remain disabled. It is possible to Restore an archived item by using the corresponding menu entry:
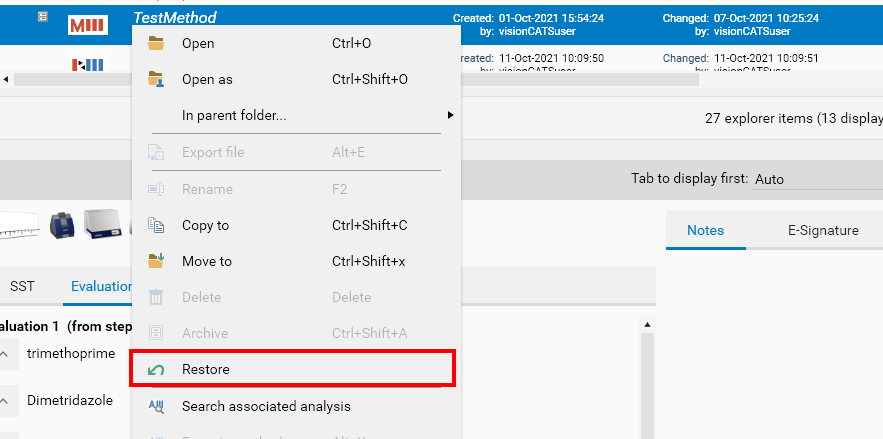
The file is then available again as any other Explorer file.
Some specific rules applies on archived items:
When folders are archived, all subfolders (recursively) and files in it are archived first. In other words, archived folders contain only archived files and subfolders. The same behavior is applied during the restoration of a folder.
In order for the Explorer to keep its consistency, it is not possible to switch from Archiving to Allow complete deletion if there are some archived items in the Explorer. If the switch still has to be done, archived items must be restored first. Note that the Advanced search feature can be used to find archived items easily. The archived items can then be restored in one operation by using the Bulk edit feature (see Menu File).
visionCATS allows to have two files with the same name in a given folder, one being a regular file and the other being an archived file. This happens when a file is created/renamed with a name already used for an archived item while the Show “Archived” items in explorer user option is deactivated. When the option is later activated, both files appear as in the capture below. To avoid inconsistencies, the archived file cannot be restored unless the regular file is renamed or moved to another folder.

Steps data loss and steps reexecution
visionCATS includes specific options regarding the deletion of executed steps’ data:

To understand the role of each option, it is necessary to recall that the execution of a step in an analysis can be interrupted:
At any time by the user, for example if the user realizes that a wrong manipulation was performed (see Execution display), or
By the HPTLC Instrument or the HPTLC PRO Module itself when an error was detected.
A step interruption, called an abort in visionCATS, is logged in the HPTLC Logger along with the pending data (images from Visualizer, profiles and spectra from Scanner) at the time the interruption occurred. Additionally, the Redo analysis operation allows to restart the analysis by deleting the data of the steps already executed.
The Allow steps data loss and steps reexecution, when deactivated, prohibits the usage of the Redo analysis operation and blocks the execution of new steps after an abort. If an abort occurs, the Instructions panel (see Chromatography) shows the corresponding information:

And in the Explorer view, the icon is displayed (see File Status). Once blocked, the analysis itself cannot be unblocked, but it is still possible to create a copy by using the
Copy to operation (see Menu File). The execution of new steps will be allowed in the copied file only if the Propagate the prohibition of execution of new steps on copied analysis is unchecked. Otherwise the
copied file will also be blocked. This last case is the strictest one, where the analysis is considered finished, without any possibility to recover, when an abort occurred. Users must then restart the execution
from the beginning in a new analysis, by using either Execute method or Redo a copy.
Motivated change
Note
This feature is only available on visionCATS installations having the 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance option.
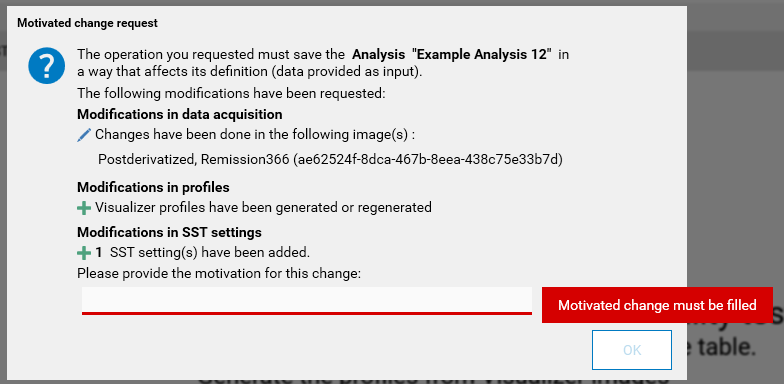
For methods and analyses, it’s possible to force users to give a reason on each save by checking the Force users to enter a reason to each change on HPTLC items option in .

When this option is checked, a save on a method or on an analysis (with the exception of saves of changes consisting exclusively in automatically computed data) always shows the Motivated changes request window, and the motivation text entered by the user is saved in the HPTLC Logger.
Open as management
Note
This feature is only available on visionCATS installations having the 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance option. Otherwise, the open as function is always activated.
If wanted, the whole open as function can be disabled. By default, it is enabled.

E-Signature
Note
This feature is only available on visionCATS installations having the 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance option.
The visionCATS software provides a custom E-Signature solution for:
methods and analyses files, which can be E-Signed directly at the file level,
comparison files, where the E-Signature is performed on individual tracks,
HPTLC instrument, HPTLC PRO Module, CAMAG® HPTLC PRO SYSTEM and visionCATS diagnostics, where the E-Signature is performed on the last diagnostics session.
To use the E-Signature feature, the User Management must be activated and the E-Signature feature must be configured in the window, sections E-Signature levels and E-Signature user rights.
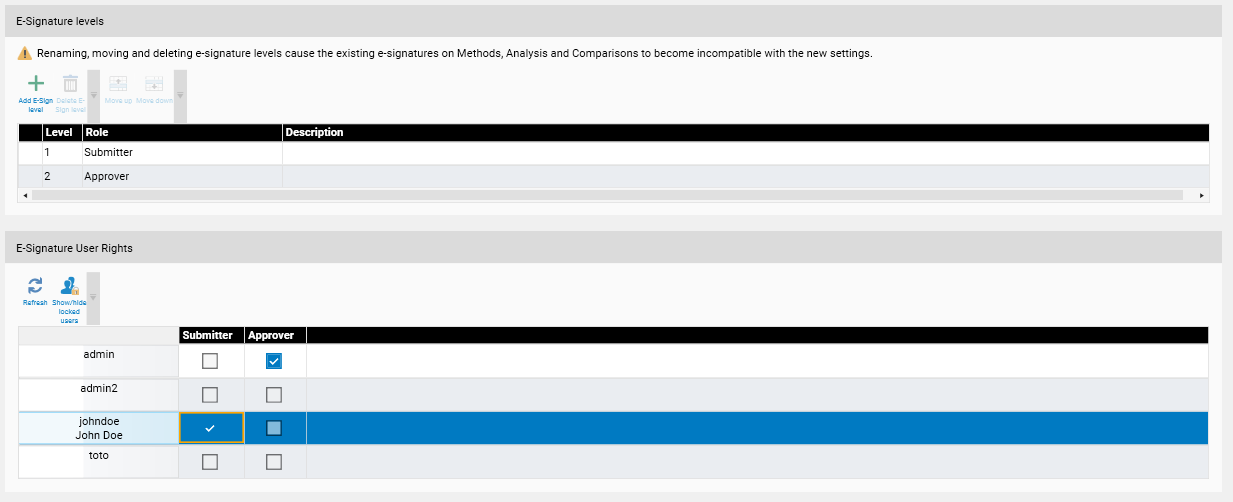
On a given file, an E-Signature starts at level 1 (called here Submitter). For each level, each user can/can’t sign files based on the items checked in the E-Signature user rights section table. A file already signed at level “n” can only be signed at level “n+1” if the level “n+1” has been defined. A user can’t sign the same HPTLC item on more than one different signing levels. Any modification to a file containing an E-Signature removes its E-Signature.
To sign a file, use the E-Sign… entry:
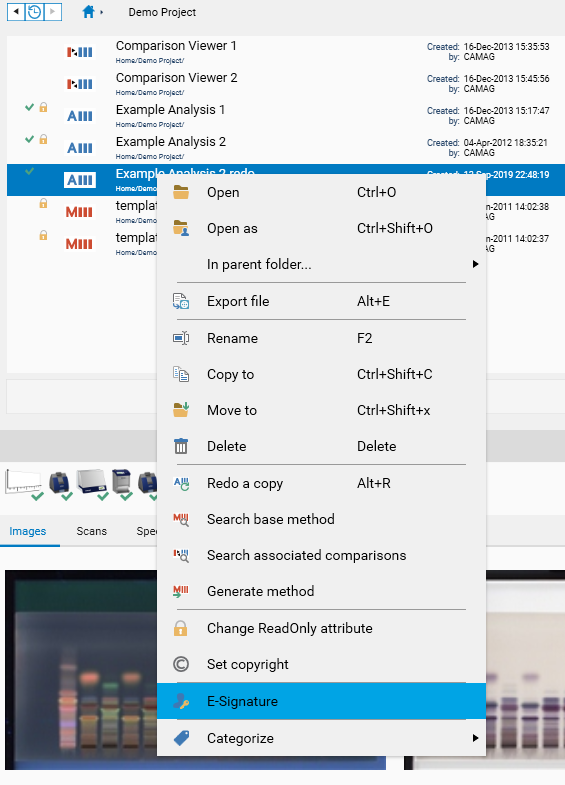
The E-Sign window always asks for credentials, and an optional comment. This information, associated with the current timestamp, constitutes the E-Signature itself.
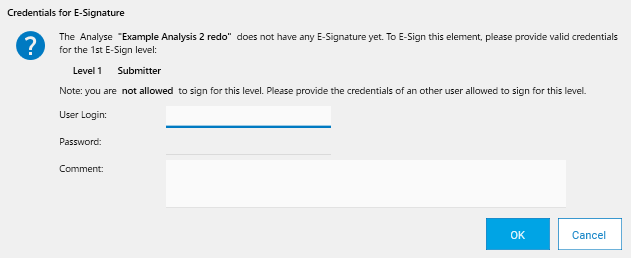
After having signed a file, any save operation in it will result in a warning, indicating that the save will delete the E-Signature. E-Signature related information is shown directly in the explorer item row itself, next to the tabs displayed inside the HPTLC item when opening it, and a complete view of the whole signature is available in the Preview area:
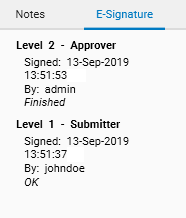
Some special rules apply to signed elements:
When the E-Signature levels or names change, existing E-Signatures are kept as-is, but it’s not possible to further sign them.
When a file is imported from a foreign system, its E-Signature is kept as-is, but it’s not possible to further sign it.
Note
To be valid across visionCATS installations on different time zones, the E-Signature date time is always stored in Coordinated Universal Time, but displayed in local time zone. Therefore, two visionCATS’ clients with different time zones would display a different time.
Data integrity
As visionCATS saves data in a specific folder on the server, data integrity should be assured from the Windows rights.
As data are stored only on the server machine, it is recommend to install visionCATS server on a dedicated machine, on which only the IT Administration has access.
Otherwise (like for standalone installation), the data in the image folder should be protected with specific user rights. For more information, see How to setup Windows user rights for data integrity.
Note
As the database files are stored in the respective installation folder, any modification of it by a standard user is already blocked by Windows.